Introduction to Healthy Diet
Healthy eating is a fundamental component of maintaining and improving health, especially in people who suffer from diseases. A balanced diet not only provides essential nutrients necessary for optimal body function, but can also speed recovery and improve overall well-being. For those facing medical conditions, a proper diet can be a powerful ally in the fight against illness.
The human body requires a variety of nutrients to carry out its daily functions. These include macronutrients such as protein, carbohydrates and fats, as well as micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. When we are sick, our nutritional needs can change, and it is crucial to adapt our diet to meet those specific demands. For example, some nutrients can play a vital role in strengthening the immune system, reducing inflammation, and repairing damaged tissues.
Additionally, a healthy diet can help prevent additional complications that often accompany chronic diseases. For example, people with diabetes should control their carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood glucose levels, while those with hypertension may benefit from a low-sodium diet. By adopting a personalized and evidence-based approach, it is possible to minimize the associated risks and significantly improve quality of life.

In short, healthy diet is more than just a lifestyle choice; It is an essential necessity for those seeking to recover from illness and maintain good long-term health. Integrating healthy eating habits can have a profound impact on the body's ability to heal and function efficiently, making nutrition an integral part of disease treatment and prevention.
Hydration is a vital component to overall well-being, especially for sick people. Maintaining proper hydration is crucial for the optimal functioning of the human body. Water plays multiple essential roles, such as regulating body temperature, eliminating toxins, and maintaining key physiological functions.
Corporal temperature regulation

One of the main benefits of adequate hydration is the regulation of body temperature. Water acts as a natural thermoregulator, allowing the body to release heat through perspiration and breathing. This is particularly important for sick people, as fevers and other symptoms can increase body temperature, requiring increased fluids to maintain thermal balance.
Elimination of toxins

Elimination of toxins is another critical function facilitated by adequate hydration. The kidneys, which are the main organs responsible for filtering and eliminating waste from the body, depend on water to function effectively. Insufficient fluid intake can lead to a buildup of toxins, which can further aggravate the patient's condition. For sick people, optimal hydration helps keep the excretory system in good condition, promoting a faster and more efficient recovery.
Maintenance of bodily functions
Water is also essential for the maintenance of various essential bodily functions. It aids in the digestion, absorption and transportation of nutrients, which is crucial for anyone's well-being, but even more so for those who are sick and have higher nutritional needs. Additionally, adequate hydration contributes to joint lubrication and maintenance of skin health, both important for patient comfort and overall recovery.
In summary, proper hydration is essential for sick people, as it contributes significantly to the regulation of body temperature, the elimination of toxins and the maintenance of essential bodily functions. Ensuring that enough fluids are consumed can make a noticeable difference in the recovery process and improving the patient's quality of life.
Contribution of Essential Nutrients
The provision of essential nutrients in a diet is a critical factor for the recovery and maintenance of health, especially in sick people. Essential nutrients include vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates and healthy fats, each of which plays a specific and vital role in the body.

Vitamins are organic compounds that the body needs in small amounts to function properly. Vitamins A, C and E are antioxidants that help protect cells from damage. Vitamin D is important for bone health and the immune system, while B vitamins are essential for energy production and brain function.
Minerals, on the other hand, are inorganic elements that are also crucial for various bodily functions. Iron is necessary for the formation of hemoglobin and the transport of oxygen in the blood. Zinc plays a critical role in immune function and wound healing. Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle contraction, while magnesium is involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body.
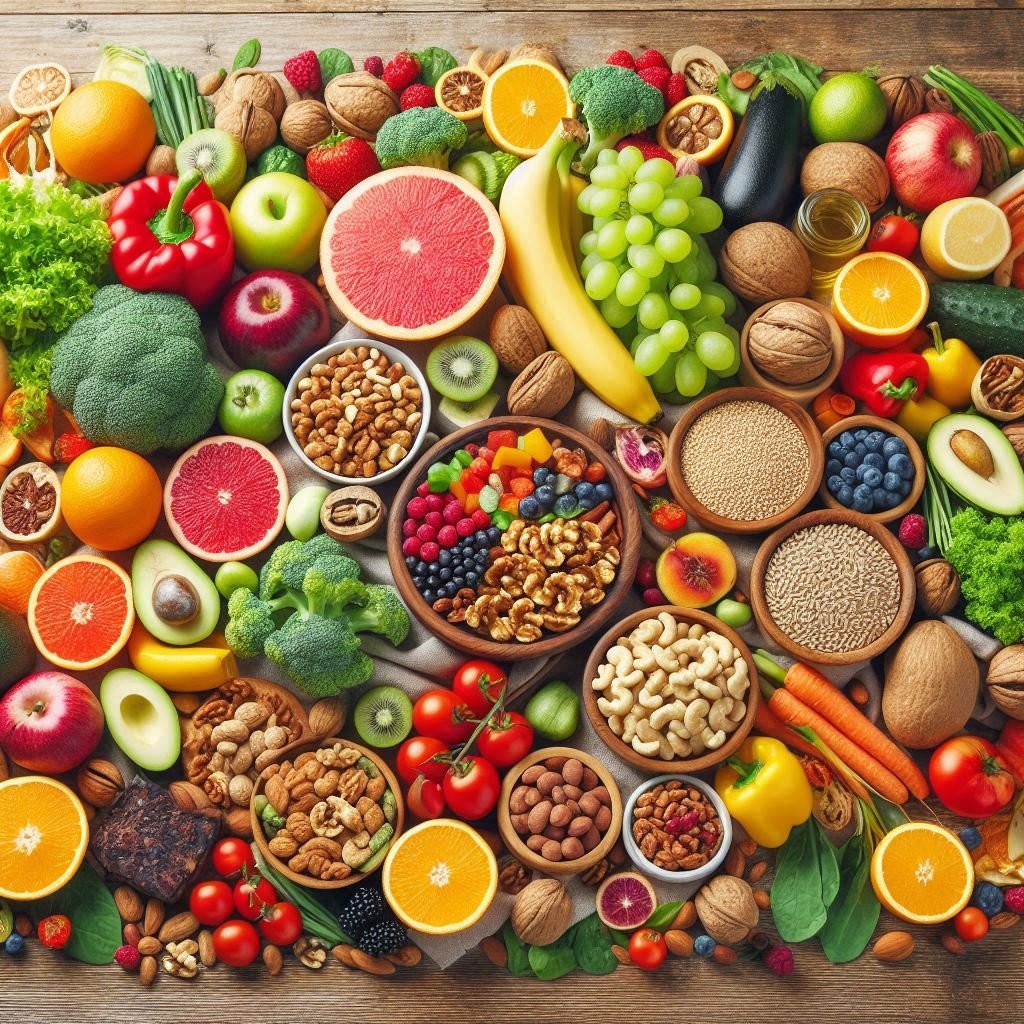

Proteins are macronutrients that are responsible for the repair and construction of tissues, the production of enzymes and hormones, and the regulation of the immune system. Protein sources can be animals, such as meat, fish and eggs, or vegetables, such as legumes, nuts and seeds.
Carbohydrates are the body's main source of energy. It is important to select complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables, which provide sustained energy and contain fiber, which benefits digestive health.

Finally, healthy fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are essential for brain function, cardiovascular health, and reducing inflammation. These fats are found in foods such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
Together, these essential nutrients contribute significantly to the recovery and maintenance of good health, providing the body with the necessary resources to fight disease and strengthen the immune system.
Foods to Avoid
When you are sick, it is essential to be selective with the foods you eat, since certain products can aggravate symptoms and delay recovery. One of the main food groups to avoid is processed foods. These products, which include fast foods, canned foods and packaged snacks, are often full of preservatives, colorings and additives that can be harmful to the body.
Additionally, foods high in sugar should be avoided. Excessive sugar consumption can weaken the immune system, making it less effective at fighting infections. Sugary drinks, cakes, cookies and other desserts are examples of products that are best left aside during illness.

Saturated fats also play a negative role in the recovery process. These fats, found in fried foods, fatty meats, and full-fat dairy products, can increase inflammation in the body. Additional inflammation can worsen symptoms and prolong the duration of the illness.
Another group of foods to avoid are those that contain high levels of sodium. Excess salt can cause fluid retention and increase blood pressure, which is especially problematic for people with pre-existing health conditions. Frozen meals, canned soups, and cold cuts are examples of foods that contain high levels of sodium.

Finally, it is advisable to avoid excessive consumption of caffeine and alcohol. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea and some energy drinks, can cause dehydration, while alcohol can weaken the immune system and interfere with the effectiveness of certain medications.
In short, avoiding these foods not only helps prevent symptom exacerbation, but also facilitates a faster and more effective recovery. Choosing fresh, natural and nutritious foods is crucial to supporting the immune system and improving overall well-being.
Meal Planning

Meal planning plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy diet, especially for sick people. A strategic approach to food selection and preparation can significantly contribute to recovery and overall well-being. It is essential to recognize the importance of regularity in meals, as eating at regular intervals can help maintain stable energy levels and improve digestion.
Another vital aspect is portion size. To avoid overloading the digestive system, it is advisable to opt for small, frequent portions instead of large meals. This not only facilitates digestion, but can also prevent discomforts such as indigestion or reflux. Sick people should pay close attention to their hunger and satiety cues to adjust portions appropriately.

Including all food groups in each meal is another fundamental principle. A balanced diet should contain a variety of foods that provide essential nutrients. Proteins are crucial for tissue repair and maintenance, so it is advisable to include sources such as lean meat, fish, eggs or legumes. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits and vegetables, provide sustained energy, while healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados and nuts, are important for cellular function and absorption. of vitamins.
Additionally, it is essential to maintain adequate hydration. Drinking enough water throughout the day helps maintain fluid balance and support bodily functions. In some cases, nutritious soups and broths can be an excellent option to increase fluid and nutrient intake.

In summary, well-structured meal planning, including regularity, portion control, and nutritional diversity, can be a powerful tool to improve the health and well-being of sick people.
Disease-Specific Adaptations
Adapting the diet to the specific needs of a disease is essential to improve quality of life and optimize medical treatment. Different health conditions require specific dietary adjustments, and it is crucial to understand which foods are beneficial and which should be avoided.
For diabetes, it is essential to control the blood glucose level. A diet rich in fiber is recommended, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes, which help stabilize sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as berries, apples, and sweet potatoes, are particularly beneficial. It is vital to avoid refined carbohydrates and added sugars, present in cakes, cookies and sugary drinks, as they can cause glucose spikes.

In the case of heart disease, a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol is crucial. Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flax seeds, can improve heart health. Other beneficial foods include green leafy vegetables, which are high in antioxidants and fiber. On the other hand, you should limit your intake of processed foods, trans fats and sodium, which can increase blood pressure and cholesterol.

For gastrointestinal problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), it is important to identify and avoid dietary triggers. A low-FODMAP diet, which restricts certain fermentable carbohydrates, may be helpful. Foods such as rice, oats and chicken are generally well tolerated, while dairy products, legumes and certain vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower, which can cause bloating and discomfort, should be avoided.
In conclusion, adjusting the diet according to the specific disease can not only alleviate symptoms, but also support medical treatment and improve quality of life. Consulting with a health professional for personalized recommendations is essential to ensure that the diet is appropriate and effective for each health condition.
Importance of Professional Support

In the context of a healthy diet for sick people, the support of health professionals such as nutritionists or dieticians is essential. These experts are trained to provide personalized meal plans that fit each patient's individual needs. Unlike general diets found on the internet, a professionally designed plan takes into account the patient's specific health condition, dietary restrictions, and personal preferences.
One of the most significant benefits of consulting a professional is the ability of these specialists to adjust your diet on an ongoing basis. Health conditions can change, and it is crucial that diet evolves with them. For example, a patient with diabetes may require adjustments to their carbohydrate intake, while someone with kidney disease may need close monitoring of sodium and protein intake. A nutritionist or dietitian can make these modifications safely and effectively, ensuring that nutritional balance is maintained.

In addition, constant monitoring by health professionals helps detect possible nutritional deficiencies and prevent complications. Through regular consultations and laboratory tests, the patient's progress can be evaluated and adjustments made as necessary to optimize results. This proactive approach not only improves the patient's quality of life, but may also reduce the need for additional medical interventions.
Finally, the emotional and educational support provided by nutritionists and dietitians is also invaluable. These professionals not only offer technical guidance, but also motivate patients to follow their eating plans and teach them skills to make healthy long-term decisions. This comprehensive support is essential to foster sustained adherence and achieve lasting results in disease management through nutrition.
Conclusion and Final Recommendations

In conclusion, maintaining a healthy diet is essential to support the recovery process during illnesses. Throughout this blog, we have discussed the general principles that should guide nutrition during these critical moments. A balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, proteins and healthy fats, can make a significant difference in the body's ability to fight illness and recover more quickly.
It is crucial to include a variety of fresh, natural foods, prioritizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. Additionally, proper hydration should not be underestimated, as water plays a vital role in almost all bodily functions, especially during illness. Avoiding processed foods, rich in sugars and saturated fats, is also an essential recommendation to maintain general well-being.
Adopting these principles of a healthy diet is not only beneficial during illness, but also contributes to the prevention of future health conditions. Conscious, balanced eating strengthens the immune system, improves energy and mood, and promotes a better overall quality of life.
We encourage readers to be proactive in their daily nutrition, paying attention to the quality and variety of the foods they consume. Consulting with health professionals, such as nutritionists or dieticians, can provide personalized guidance and ensure that appropriate dietary decisions are being made based on individual needs.
In summary, correct nutrition during illness is a fundamental pillar for an effective and sustained recovery. By incorporating these principles into daily life, long-term health and well-being can be significantly improved.
Maybe you might like: Homemade Tomato Sauce Recipe: Easy, Quick and Delicious
Credit images Bing Images Create


